What is Thalassemia?
Thalassemia
- Thalassemia is an inherited blood disorder (passed from parents to children through genes). Anaemia is a disorder in which your body doesn’t have enough normal, Red Blood Cells (RBC).
- Overall estimate of B – Thalassemia carriers is 35-45 million among lndia’s population of over a billion people .
- Estimated number of births of affected babies annually would be 10,000-12,000; causing a social, Psychological and financial burden
The major Hemoglobin Disorders
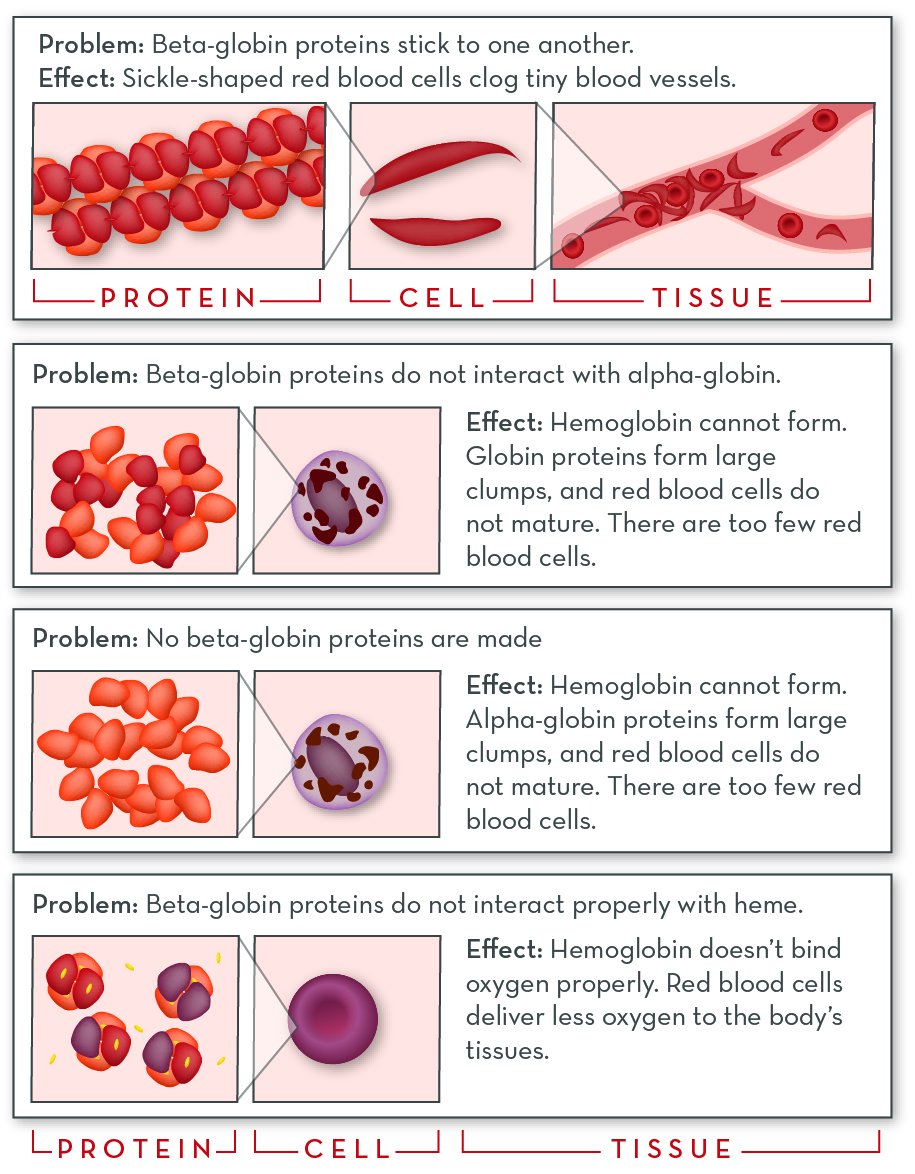
Social, Psychological and financial Burden
Thalassemia challenges the individual at the Physical, emotional, cognitive levels and disrupts the quality of life.
What are the different types of Thalassemia ?
When we talk about different type “thalassemia”; we refer about one of two things: the specific part of hemoglobin that is affected (usually either “alpha’’ or ‘’beta’’), or the severity of thalassemia, which is noted by words like trait, carrier intermedia or major.
Hemoglobin, which carries oxygen to all cells in the body, is made of two different parts, called alpha and beta.
When thalassemia is called ‘’alpha’’ or ‘’beta,’’ this refers to the part of hemoglobin that isn’t being made. If either the alpha or beta part is not made, there aren’t enough building blocks to make normal amounts of hemoglobin.
Low alpha is called alpha thalassemia
Low beta is called beta thalassemia.
When the words “trait”, “minor”, “intermedia’’, or “major’’ are used, these words describe how severe the thalassemia is. A person who has thalassemia
trait may not have any symptoms at all or may have only mild anaemia, while a person with thalassemia major may have severe symptoms and may need regular blood transfusions.
What is Thalassemia minor ?
People with a thalassemia mutation only in one gene are known as carriers or are said to have thalassemia minor. Thalassemia minor results in no
anaemia or very slight anaemia, people who are carriers do not require blood transfusion or iron therapy, unless proven to be iron deficient.
What is Thalassemia major ?
Children born with thalassemia major usually develop the symptoms of severe anemia within the first year of life. Lacking the ability to produce normal adult hemoglobin, children with thalassemia major:
o Are chronically fatigued
o Fail to thrive, and
o Do not grow normally
How do you inherit Thalassemia ?
If both parents carry thalassemia minor, their children may have thalassemia minor, or they may have completely normal blood, or they may have thalassemia major:
In each pregnancy there is a one in four (25%) chance that their child will have normal blood, a two in four (50%) chance that the child will have thalassemia minor or a one in four (25%) chance that the child will have thalassemia major.
How is Thalassemia diagnosed ?
Thalassemia is diagnosed by the following tests:
1) Complete Blood count (CBC with blood smear)
2) Iron studies
3) Haemoglobinopathesis (Hb) Evaluation: This test measures the type and relative amounts of hemoglobin present in the red blood cells. Haemoglobin A, composed of both alpha and beta globin, is the normal type of hemoglobin Found in adults. A greater percentage of Hb A2 and/or f is usually seen in beta thalassemia trait. Hb H may be seen in alpha thalassemia due to Hb H disease. Other Haemoglobinapathesis -HbD, HbE, HbS
4) DNA Analysis: This test is used to investigate deletions and mutations in the alpha and beta globin producing genes. DNA testing is not routinely done but can be used to help diagnose thalassemia and to determine carrier status.
How is Thalassemia treated ?
The treatment for thalassemia depends on the type and severity of disease involved. Your doctor will give you a course of treatment that is customized to your particular case.
Visit the Mundial group page
Comments
Post a Comment